Estimated Reading Time: 30-33 minutes (5,948 words)
Introduction
Electric vehicles (EVs) have moved far beyond being a futuristic concept — in some parts of the world, they are quickly becoming the default mode of transportation. Nowhere is this more evident than in Norway, which in 2025 set a world record when 95.9% of all new passenger cars registered were fully electric (World Auto Forum). To put this in perspective, while most countries are still grappling with EV adoption rates in the single digits or low tens, Norway’s market has almost completely shifted away from internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles.
This rapid electrification is not a coincidence. It is the result of a carefully orchestrated mix of government policies, cutting-edge technology, strategic infrastructure investments, and an environmentally conscious consumer base. Norway’s model shows how a country can transform an entire automotive market in under a decade, proving that EV adoption is not only possible but highly scalable under the right conditions.
In this post, we dive deep into how Norway achieved this historic milestone, exploring everything from policy incentives and charging infrastructure to consumer behavior and top-selling EV brands. We also examine the global context, comparing Norway’s EV success with other regions like China, Europe, and the United States, and discuss what these lessons mean for emerging markets such as India, which are in the early stages of the EV revolution. By the end, readers will gain a comprehensive understanding of Norway’s EV dominance, the global EV landscape, and practical insights for accelerating EV adoption in other markets.
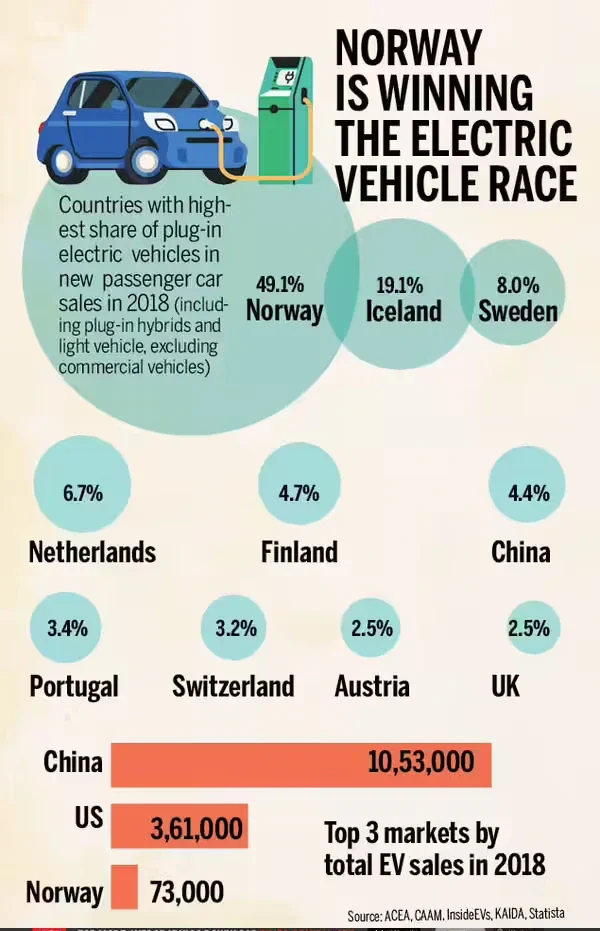
Key Facts & Statistics
Norway’s 2025 EV market performance is nothing short of historic, cementing its place as the global leader in electric mobility. Let’s break down the numbers, brand performance, and long-term trends that define this remarkable shift.
📊 Norway EV Sales in 2025
- Overall EV Market Share: In 2025, 95.9% of all new passenger cars registered in Norway were fully electric, up from 88.9% in 2024 (World Auto Forum). This near-total dominance is a stunning leap compared to other European markets, where EV adoption still hovers in the 10–30% range.
- December 2025 Peak: During December alone, almost 98% of new car sales were electric, highlighting Norway’s seasonal surge in EV adoption, likely influenced by policy deadlines, model availability, and consumer incentives. This represents practically a full switch to electric vehicles in one of the world’s wealthiest and most environmentally conscious nations.
- Total Registrations: Norway registered 179,549 new cars in 2025, marking a 40% increase compared to 2024 (World Auto Forum). This surge indicates that EV adoption is not just a niche market phenomenon, but a mainstream transition, embraced by consumers across income levels and urban-rural segments.
🚗 Top EV Brands in Norway (2025)
The Norwegian EV market is dominated by a mix of global and regional automotive leaders, with Tesla leading the charge:
| Rank | Brand | Market Share | Key Insights |
| 1 | Tesla | ~19.1% | The Model Y was especially popular, offering long range, advanced autopilot, and strong brand appeal. Tesla’s Supercharger network also ensured convenience and reliability, reinforcing its market leadership. (ETBrandEquity) |
| 2 | Volkswagen | ~13.3% | VW’s ID.4 and other models gained traction due to affordable pricing, strong battery range, and European brand recognition. |
| 3 | Volvo | ~7.8% | Scandinavian brand with safety and sustainability appeal, favored by Norwegian consumers. |
| 4 | BYD & Other Chinese Brands | ~5–6% combined | Gaining ground due to affordable pricing and expanding European market presence. |
This distribution highlights Norway’s openness to both premium and mid-range EVs, balancing performance, affordability, and sustainability.
📈 Historical EV Trend (2012–2025)
Norway’s EV adoption over the last decade illustrates one of the fastest automotive transformations in history:
- 2012: EVs accounted for only ~2.8% of new car registrations. Adoption was driven primarily by early adopters and government incentives.
- 2015: Market share reached ~15%, coinciding with the expansion of public charging infrastructure.
- 2018: EV share surpassed 30%, and Norway became the first country where EVs overtook diesel in some months.
- 2020: EVs made up ~54% of new registrations, marking the transition from niche to mainstream.
- 2024: EV adoption climbed to ~88.9%, showing strong consumer trust and policy effectiveness.
- 2025: Nearly 96% of new cars were electric, culminating in Norway’s global leadership. (Wikipedia)
Key Insight: This trend demonstrates that with consistent policy support, infrastructure expansion, and public awareness, a country can electrify nearly its entire new car market in just 13 years—an unprecedented case study for the rest of the world.
💡 Quick Facts Box: Norway EV Market 2025
- EV share of new registrations: 95.9%
- December 2025 EV share: ~98%
- Total new car registrations: 179,549 (+40% YoY)
- Top-selling EV brand: Tesla (~19.1%)
- Other leading brands: Volkswagen (~13.3%), Volvo (~7.8%)
- Decade-long EV growth: From 2.8% (2012) → 95.9% (2025)
Why Norway Leads the EV Race
Norway’s dominance in the electric vehicle market did not happen overnight. It is the result of a strategic combination of government policy, infrastructure investment, and cultural mindset that has created one of the world’s most EV-friendly environments. Let’s break down the core factors behind Norway’s EV success in detail:
A. Strong Government Incentives
Norway has consistently provided one of the most generous incentive programs in the world for electric vehicles. These incentives are designed to make EVs financially competitive with, or even cheaper than, internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles:
- Tax Exemptions: EV buyers are exempt from VAT (Value Added Tax) and import duties, which can reduce the purchase price by 20–30%.
- Toll and Congestion Benefits: EV owners enjoy free access to toll roads, bridges, and ferry crossings, often saving thousands of dollars per year.
- Parking Privileges: Many municipalities provide free or discounted parking for EVs in city centers.
- Other Perks: EVs have priority access to bus lanes, reducing commuting time in busy urban areas.
These measures dramatically lowered the total cost of ownership and removed one of the biggest barriers to EV adoption: upfront purchase cost. (Wikipedia)
B. Penalty for Fossil Cars
Norway’s approach didn’t stop at rewarding EV adoption—they also discouraged fossil fuel vehicles through high taxation and penalties:
- High Registration Taxes: Petrol and diesel cars are subjected to heavy registration and import taxes, making them significantly more expensive than EVs.
- Fuel Taxes: Norway imposes high fuel excise duties, increasing the long-term operating costs of ICE vehicles.
- Gradual Phase-out: Over time, Norway has reduced incentives for fossil cars and increased incentives for EVs, creating a clear financial motivation for consumers to switch.
This dual strategy of “push” (penalize ICE) and “pull” (incentivize EVs) has been pivotal in driving rapid adoption.
C. Mature Charging Infrastructure
Even with strong incentives, EV adoption can stall if drivers fear running out of power. Norway tackled this head-on by investing heavily in a robust, reliable charging network:
- Urban Fast Chargers: Cities are equipped with fast and ultra-fast chargers, allowing drivers to recharge in 20–40 minutes.
- Rural Accessibility: Norway ensures charging stations are available along highways and in remote regions, eliminating range anxiety for long-distance travel.
- Public and Private Partnerships: Investments by both government and private companies (like Tesla Superchargers) expanded network density and reliability.
- Future-proofing: Norway continues to plan for higher-capacity chargers and integration with renewable energy, ensuring that EV adoption scales sustainably.
A well-planned infrastructure is a key reason why Norwegians confidently embrace EVs, even for long trips or cold-weather conditions.
D. Rising Consumer Awareness and Cultural Mindset
Perhaps the most powerful driver of Norway’s EV success is public perception and cultural acceptance:
- Environmental Consciousness: Norwegians have a strong commitment to sustainability, reducing carbon footprints, and supporting clean energy. EVs are seen as a responsible choice rather than a luxury option.
- Social Norms: As EV ownership became common, buying an electric car became the “default” decision rather than an alternative.
- Education and Awareness Campaigns: Government and NGOs have actively promoted EV benefits, from lower running costs to environmental impact.
- Positive Feedback Loop: Seeing neighbors, friends, and colleagues adopt EVs encourages more people to switch, creating rapid social adoption momentum.
This combination of financial, logistical, and cultural factors has allowed Norway to reach an unprecedented 95.9% EV share in new car sales in 2025. In essence, the country created a self-reinforcing ecosystem that makes switching to electric not just appealing, but almost inevitable.
💡 Key Insight
Norway’s EV leadership shows that policy alone is not enough—it must be coupled with infrastructure and a supportive cultural mindset. By addressing financial barriers, providing reliable charging, and fostering widespread environmental awareness, Norway has created the world’s most advanced EV ecosystem, offering a blueprint for other countries, including India, aiming to accelerate EV adoption.
EV Market Breakdown: Top Brands & Models
Norway’s EV market in 2025 is dominated by a mix of global automotive giants and emerging brands, reflecting both consumer preference and competitive innovation. Here’s a detailed breakdown:
📊 Top EV Brands in Norway (2025)
| Rank | Brand | Approx. Market Share | Key Models & Insights |
| 1 | Tesla | ~19.1% | Tesla continues to lead Norway’s EV market, with the Model Y being the most popular due to its long range, performance, and advanced autopilot features. Tesla’s success is also supported by its Supercharger network, which reduces range anxiety and encourages long-distance travel. Tesla’s strong brand appeal positions it as a premium, aspirational choice among Norwegian buyers. (ETBrandEquity) |
| 2 | Volkswagen | ~13.3% | VW’s ID.4, ID. Buzz, and other models appeal due to affordability, practical range, and European brand trust. Volkswagen focuses on mid-range family-friendly EVs, which are well-suited for urban commuting and small-family use. VW’s gradual rollout of EV models and competitive pricing make it Norway’s second-strongest EV player. |
| 3 | Volvo | ~7.8% | Volvo’s XC40 Recharge and other models leverage Scandinavian safety reputation and environmentally conscious branding. Volvo attracts consumers who prioritize luxury, safety, and sustainability, aligning with Norway’s eco-conscious market. |
| 4 | BYD & Other Chinese Brands | ~5–6% combined | Chinese manufacturers like BYD are gaining traction, offering affordable EV options with competitive range and features. These brands are expanding in Norway as global supply chains improve and consumer awareness grows for budget-friendly EVs. |
📈 Market Dynamics and Trends
- Premium vs Affordable EVs: Norway’s EV buyers span high-income households buying Tesla and Volvo and middle-income buyers opting for VW or BYD models, showing a broad market penetration.
- Model Popularity: SUVs dominate the market, particularly Tesla Model Y, Volkswagen ID.4, and Volvo XC40 Recharge, reflecting Norwegian preference for spacious and practical EVs suitable for urban and rural use.
- Emerging Players: Smaller European startups like Polestar and Cupra Born are beginning to capture niche segments with innovative designs and performance-focused models.
- Chinese EV Expansion: As affordability improves and European operations expand, brands like BYD, NIO, and XPeng are expected to gain a larger market share in the next 3–5 years.
- Second-hand EV Market Growth: Increasing EV sales are feeding a robust second-hand EV market, making electric vehicles accessible to younger buyers and first-time car owners.
🌍 Global Context
Norway’s EV brand dominance contrasts with other leading markets:
- China: BYD leads with affordable options; Tesla also strong, but EV adoption is younger and more price-sensitive.
- EU Average: Volkswagen dominates many European markets, but Tesla and local brands like Renault and Peugeot have stronger presence in certain countries.
- USA: Tesla dominates ~70–75% of EV sales, but market penetration is far lower overall (~10% of new cars).
Norway stands out not just for overall EV adoption, but also for balanced brand competition: both premium and mid-range EVs thrive, fostering innovation and consumer choice.
💡 Quick Insights
- Tesla: Premium, high-performance leader
- Volkswagen: Mid-range, practical, and affordable
- Volvo: Safety-focused, sustainable Scandinavian choice
- Chinese brands: Cost-effective options gaining traction
- Market trend: SUVs dominate, second-hand EVs are growing, smaller startups are emerging
How Norway’s Policies Fueled Adoption
Norway’s journey to becoming the world leader in EV adoption is not just about consumer choice—it is deeply rooted in forward-thinking government policies. Over the last decade, the Norwegian government has carefully crafted a suite of incentives and regulations that made EVs financially, logistically, and socially appealing. Let’s break down the policies that accelerated EV adoption in detail:
1. Zero Import & VAT Taxes on EVs
One of the most powerful drivers of Norway’s EV market has been the removal of purchase-related taxes:
- Import Duty Exemption: Imported EVs are exempt from hefty import tariffs, which can be as high as 25–30% for conventional cars.
- VAT (Value Added Tax) Waiver: New EVs are exempt from the 25% VAT applied to most consumer vehicles.
- Impact: These exemptions significantly reduced the upfront purchase cost, making EVs not only competitive with petrol and diesel vehicles but often cheaper than ICE alternatives.
- Result: Even premium EVs like the Tesla Model Y became attainable for many Norwegian households.
(Wikipedia)
2. Toll, Congestion, & Parking Benefits
Norway recognized that ownership costs go beyond the purchase price. To further incentivize EV adoption, the government implemented daily operational perks:
- Free Toll Roads and Bridges: EV drivers are exempt from tolls on highways, bridges, and tunnels, which can save thousands of dollars annually for commuters.
- Bus Lane Access: EVs can use priority lanes, dramatically reducing commute times in urban centers like Oslo and Bergen.
- Parking Benefits: Many municipalities offer free or discounted parking, especially in city centers and high-demand areas.
- Impact: These perks create tangible, day-to-day savings, enhancing the economic appeal of EVs beyond the initial purchase price.
3. Environmental Regulations & Long-Term Targets
Norway’s policies go beyond financial incentives—they are guided by a strong environmental agenda:
- Zero-Emission Vehicle Target: Norway committed to phasing out fossil fuel cars and achieving near-total EV sales for new passenger vehicles by 2025.
- Carbon Emission Reductions: Strict environmental regulations penalize high-emission vehicles, encouraging consumers and businesses to choose EVs.
- Alignment with Climate Goals: Policies align with Norway’s broader commitments under the Paris Agreement and national decarbonization strategies.
- Result: Environmental consciousness is reinforced at both societal and regulatory levels, creating a culture where EVs are the default choice.
4. Phasing Out Incentives Thoughtfully
As EV adoption approached saturation, Norway began gradually adjusting incentives to ensure long-term sustainability:
- Reduction of Certain Tax Exemptions: Some VAT exemptions and perks have been slightly reduced in recent years.
- Maintaining Competitiveness: Even with reduced incentives, EVs remain financially favorable due to lower running costs, free tolls, and continued infrastructure support.
- Purpose: The phased approach prevents market shock, ensures government budgets remain sustainable, and prepares consumers for a future where EVs compete more directly with ICE vehicles.
- Impact: This careful policy evolution ensures that EV adoption continues naturally, without relying solely on financial incentives.
(Reddit discussion)
💡 Key Insight
Norway’s policy success lies in combining upfront financial incentives with daily operational perks, long-term environmental targets, and gradual policy evolution. The result is a self-reinforcing system: incentives attract new buyers, infrastructure supports use, regulations create societal pressure, and cultural acceptance accelerates adoption. This holistic policy approach offers a blueprint for countries like India, where strategic subsidies, charging infrastructure, and phased regulation could similarly drive rapid EV adoption.
Global EV Market Comparison (2025 Trends)
While Norway’s achievement of nearly 96% electric vehicle (EV) sales in 2025 stands as an extraordinary outlier, the global EV landscape tells a more varied story. EV adoption rates, growth patterns, and market dynamics differ significantly by region — shaped by government policies, infrastructure readiness, consumer behavior, and OEM competitiveness.
🌍 Global EV Sales Growth in 2025
- Worldwide EV sales reached record levels, with strong gains in China and Europe driving much of the growth. Total EV deliveries are estimated at over 17–18 million units in 2025, marking year‑on‑year increases of ~25–30%. China alone accounts for a majority share — more than 60% of global EV sales. China also exported over 1 million new energy vehicles (NEVs) in the first half of 2025, underlining its role as the dominant EV production hub. Battery Tech+1
- Europe’s EV market grew steadily, capturing roughly 17–20% of all new vehicles sold in 2025 in key regions like the EU, UK, and EFTA, driven by stricter emission regulations and broader model availability. EVwire
- In contrast, North America lagged behind, with slower EV uptake due to policy changes (e.g., removal of certain EV incentives in the U.S.) and stronger consumer preference for traditional trucks and SUVs — ultimately lowering EV share to the low single digits in late 2025. Reuters
📊 EV Adoption Share: Norway vs. Global Regions
| Region / Market | EV Share of New Vehicles (approx.) | Context |
| Norway | ~95.9% | World leader with near‑complete EV transition in new car sales. ETBrandEquity.com |
| China | ~30–35% | Largest EV market by volume; strong domestic demand and exports. EVwire+1 |
| Europe (EU + UK) | ~17–20% | Growing adoption, but mixed policy support has led to varied outcomes. EVwire |
| North America | ~7–10% (U.S. specific) | Adoption constrained by weaker incentives and preference for ICE vehicles. Reuters |
| Rest of World | ~10–15% | Fast growth in emerging markets, albeit from a low base. EVwire |
Key Insight: Norway’s near‑universal EV adoption is far ahead of other markets, where EVs are gaining share but still represent a fraction of total vehicle sales.
🚗 Tesla vs. BYD: Global EV Brand Leadership
One of the most noteworthy developments in the global EV market in 2025 was the shift in leadership among EV manufacturers:
- BYD overtook Tesla as the world’s largest seller of battery electric vehicles (BEVs) in 2025, selling roughly 2.26 million EVs globally — about a 28% increase from the previous year. Meanwhile, Tesla’s deliveries were estimated at around 1.6–1.7 million units, marking a significant shift in global dominance. Barron’s+1
- BYD’s success stems from a diverse lineup of affordable EVs, strong domestic demand in China, and rapidly expanding export markets across Asia, Europe, and Latin America. Tesla — historically the EV market leader — faced slowing growth amid increased competition and shifting incentive policies in key markets. Barron’s

🌐 Regional Differences in EV Adoption Patterns
- China: Remains the largest EV market by volume, with millions of annual EV sales and sustained growth driven by local OEMs, strong manufacturing ecosystems, and supportive policy frameworks. China’s EV share significantly outpaces most other regions. Electrek
- Europe: Despite strong environmental policy ambitions, some member states have revised or delayed future ICE bans, and overall EV growth is subject to policy consistency and infrastructure rollout timelines. ETBrandEquity.com
- North America: EV adoption grew more slowly, partly due to reduced federal incentives (e.g., U.S. EV tax credits expired in late 2025) and higher consumer preference for traditional ICE models like pickups and SUVs. Reuters
- Emerging Markets: Many regions in Asia, Latin America, and Africa are now seeing rapid year‑on‑year EV sales growth — though from a lower base. Chinese EV exports are playing a significant role in expanding EV adoption globally. EVwire
💡 Why Norway’s Example Is Unique
Norway’s performance — nearly 96% of new car sales being electric in 2025 — is a global outlier. This dominance cannot be attributed to global trends alone — it reflects deliberate and effective national policies, comprehensive charging infrastructure, and a culture that embraces sustainable mobility. In most other countries, even strong EV markets hover in the 20–35% range for new EV sales, underscoring how far ahead Norway is compared to global peers. ETBrandEquity.com
What This Means for India
While Norway has already achieved near-total EV adoption, India is at an earlier stage of the electric vehicle revolution — yet the growth trajectory is promising. Understanding Norway’s success provides valuable lessons for accelerating India’s EV transition.
📈 India EV Trends (2025)
- Market Share: In 2025, electric four-wheelers accounted for approximately 3.7% of total passenger vehicle sales, a significant jump from ~1.5% in 2023 (EVwire).
- Year-on-Year Growth: EV sales in India grew by 46.2% in the first half of 2025, reflecting rising consumer awareness, more EV model availability, and expanding government support (EVwire).
- Government Initiatives: Policies such as FAME (Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Hybrid and Electric Vehicles) Phase II, along with state-level incentives for EV purchases and infrastructure, are boosting adoption. Benefits include:
- Upfront subsidies for electric cars and two-wheelers.
- Incentives for manufacturers to localize EV production.
- Tax breaks and lower registration fees for EVs.
- Charging Infrastructure Growth: India’s public charging network is expanding, particularly along highways and urban centers, though it remains limited compared to Norway’s dense, nationwide network.
💡 Key Lessons from Norway for India
- Incentives Drive Adoption, but Sustainability Matters
Norway demonstrates that financial incentives, tax exemptions, and toll benefits can rapidly increase adoption. India’s FAME scheme is a step in the right direction, but long-term affordability and policy stability are essential to maintain growth. - Charging Infrastructure Is Critical
Even generous incentives cannot overcome range anxiety. Norway’s success was underpinned by a robust nationwide charging network, including fast chargers in cities and rural areas. India must prioritize charging infrastructure, integrating public, private, and highway charging solutions. - Consumer Awareness & Cultural Shift
Norwegian consumers embraced EVs as the “default” choice, reflecting both environmental consciousness and economic sense. In India, awareness campaigns emphasizing cost savings, environmental impact, and technological benefits can help normalize EV ownership. - Regulation + Incentives Work Together
Norway’s dual strategy — rewarding EV buyers and penalizing fossil fuel vehicles — accelerated adoption. India could explore graduated ICE vehicle taxation or congestion-based fees to complement EV incentives. - India’s Market Potential Is Huge
With over 4 million passenger vehicle sales annually, even a small increase in EV adoption can translate into significant volumes. Targeted incentives, localized EV manufacturing, and infrastructure development could rapidly scale adoption, similar to Norway, albeit at a larger population and income-diverse market.
🔑 Summary Insight for India
- India’s EV market is growing fast but remains nascent compared to global leaders like Norway.
- Policy clarity, incentives, and infrastructure development are critical levers to accelerate adoption.
- Norway’s model provides a blueprint: strong financial support, accessible infrastructure, and regulatory reinforcement create a self-sustaining EV ecosystem.
With strategic planning and investment, India’s massive automotive market could transition to electric vehicles faster than anticipated, creating opportunities for manufacturers, policymakers, and consumers alike.
Challenges in Norway’s EV Transition
Even with unprecedented success, Norway’s electric vehicle (EV) journey is not without complex challenges. Maintaining and scaling near-universal EV adoption requires careful management of infrastructure, market dynamics, and policy adjustments. Here’s a detailed look at the main hurdles:
A. Infrastructure Load & Grid Pressure
Norway’s widespread EV adoption puts tangible pressure on the national electricity grid and public charging networks:
- High Charging Demand: With nearly 96% of new cars being electric in 2025, fast-charging stations in urban and suburban areas experience peak-time congestion, leading to wait times and occasional outages.
- Grid Stability: Concentrated EV charging, especially during winter evenings when energy demand peaks, can strain the electrical grid, requiring upgrades and smart load management.
- Rural Access Challenges: While urban coverage is robust, rural and remote regions still face limited charging points, which may impact long-distance EV travel.
- Solutions: Norway is investing in grid modernization, smart charging systems, and renewable energy integration to meet rising demand while maintaining reliability.
B. Incentive Adjustments & Market Response
Norway’s policy-driven EV adoption comes with the risk of market sensitivity to changing incentives:
- Gradual Tax Reintroduction: As the government phases out some EV incentives and reintroduces partial registration or VAT taxes, some consumers may delay purchases, hoping for better deals or considering ICE alternatives. (Reddit)
- Price Sensitivity: Even with strong cultural support for EVs, higher purchase prices could slow the momentum of new EV registrations, especially for mid-range buyers.
- Manufacturer Response: OEMs need to adjust pricing, model availability, and promotions to maintain steady sales in response to changing policies.
C. Second-hand EV Market Dynamics
With a high penetration of EVs, Norway faces challenges related to used EV sales:
- Market Saturation: As more EVs age and enter the second-hand market, prices for new EVs may face downward pressure.
- Battery Degradation Concerns: Buyers of second-hand EVs often worry about battery lifespan and replacement costs, which can affect overall market confidence.
- Policy Implications: Norway may need regulations or incentives to balance the growth of new and used EV sales, ensuring manufacturers remain profitable while consumers benefit.
- Opportunity: A growing second-hand EV market also provides affordable options for younger buyers, supporting overall EV adoption growth.
D. Additional Emerging Challenges
- Supply Chain Pressure: High demand strains battery production, semiconductor availability, and EV component supply, potentially delaying new model deliveries.
- Winter Performance: Cold-weather performance can reduce EV battery efficiency, requiring advanced thermal management and public awareness.
- Urban Planning: Increased EV traffic necessitates smart city planning, including dedicated EV lanes, parking, and charging hubs to avoid congestion.
💡 Key Insight
Norway’s EV success demonstrates that even a near-perfect adoption scenario faces operational, economic, and market challenges. While policy, infrastructure, and consumer preference have created a near-ideal ecosystem, continuous investment in charging networks, grid upgrades, and thoughtful incentive management is critical to maintaining momentum. The Norwegian experience shows that long-term EV transition requires balancing growth with sustainable infrastructure and market planning — lessons highly relevant for emerging markets like India.
10‑Year EV Outlook (2026–2036)
The next decade promises to be transformative for global electric vehicle (EV) adoption, with major implications for consumers, manufacturers, policymakers, and emerging markets like India. While Norway has already reached near-total EV penetration, other countries are rapidly ramping up adoption as technology, incentives, and infrastructure improve.
🌍 Global EV Projections (2026–2036)
- Global EV Share: According to multiple industry forecasts, including McKinsey & Company and IEA, EVs are expected to account for over 40% of all new passenger car sales by 2030, potentially rising to 60–70% by 2035 under strong policy and technological growth scenarios.
- Leading Markets:
- China: Will remain the largest EV market by volume, driven by domestic OEMs such as BYD, NIO, XPeng, and expanding EV exports. Forecasts indicate EV penetration of 50–60% of new car sales by 2030, with the government maintaining strong incentives and charging infrastructure.
- European Union: EU countries will continue leading in EV share percentages, with Norway, the Netherlands, Germany, and France achieving 50–80% new EV sales by 2030 thanks to aggressive emission regulations and infrastructure investments.
- United States: EV adoption will grow steadily to 30–40% of new car sales by 2030, driven by federal and state incentives, corporate fleet electrification, and increased vehicle model availability.
- China: Will remain the largest EV market by volume, driven by domestic OEMs such as BYD, NIO, XPeng, and expanding EV exports. Forecasts indicate EV penetration of 50–60% of new car sales by 2030, with the government maintaining strong incentives and charging infrastructure.
- Technology Drivers: Advances in battery density, fast charging, vehicle-to-grid integration, and declining EV costs will accelerate adoption globally. Smart grids and renewable energy integration will further enhance the sustainability of EV ecosystems.
🇮🇳 India’s EV Outlook (2026–2036)
India’s EV market is at an early but rapidly expanding stage, with unique market dynamics and opportunities:
- Passenger Vehicles: Under strong policy support, EVs could account for 30–40% of new four-wheeler sales by 2035, driven by FAME subsidies, tax incentives, and rising consumer awareness. Adoption may accelerate in metropolitan areas like Delhi, Mumbai, Bengaluru, and Hyderabad, where charging infrastructure is expanding rapidly.
- Two-Wheelers & Three-Wheelers: The bulk of EV adoption in India is expected to occur in the two-wheeler and three-wheeler segments, which represent low-cost, high-volume mobility solutions. E-scooters, electric motorcycles, and electric rickshaws are already gaining popularity in urban centers and smaller towns. Forecasts suggest that EV two-wheeler sales could reach 50–60% of total two-wheeler sales by 2030, creating a strong foundation for overall market electrification.
- Infrastructure & Grid Readiness: India will need rapid scaling of public and private charging networks, grid modernization, and battery-swapping solutions to support mass EV adoption, particularly in tier-2 and tier-3 cities.
- Emerging Opportunities:
- Local Manufacturing: Government initiatives like the PLI (Production-Linked Incentive) scheme for EVs and batteries are expected to boost domestic EV production, reduce import dependency, and lower costs.
- Corporate Fleets & Ride-Hailing: Adoption in ride-hailing services (Ola Electric, Uber Electric) and delivery fleets will accelerate EV penetration while creating high-visibility use cases for consumers.
- Local Manufacturing: Government initiatives like the PLI (Production-Linked Incentive) scheme for EVs and batteries are expected to boost domestic EV production, reduce import dependency, and lower costs.
📈 Key Trends for 2026–2036
- Battery Cost Reduction: Lithium-ion battery costs are expected to drop below $100/kWh by 2030, making EVs cost-competitive with ICE vehicles even without incentives.
- Policy Harmonization: Strong alignment between federal policies, state incentives, and local infrastructure investment will determine adoption speed.
- Second-Hand Market Growth: As EV adoption rises, a robust pre-owned EV market will emerge, expanding accessibility for first-time and budget-conscious buyers.
- Technological Leapfrogging: Innovations such as solid-state batteries, wireless charging, and AI-assisted fleet management will transform EV adoption dynamics globally.
💡 Key Insight
The next decade will be critical for global EV transformation. While Norway sets the benchmark with near-total adoption today, countries like India have the potential to leapfrog through targeted incentives, infrastructure investment, and mass-market EV availability. By 2035, EVs could constitute a significant portion of both personal and commercial vehicle fleets, fundamentally reshaping transportation, energy consumption, and urban mobility patterns.
FAQs Section
1. Why is Norway’s EV adoption so high?
Norway’s extraordinary EV adoption is the result of a perfect storm of policy, infrastructure, and consumer mindset. Key factors include:
- Generous incentives: EV buyers enjoy exemptions from VAT, import taxes, and registration fees, which reduces upfront costs by 20–30% compared to conventional cars.
- Penalties for fossil fuel cars: Petrol and diesel vehicles are heavily taxed, making EVs more economically attractive.
- Infrastructure: Norway has an extensive network of fast chargers and urban charging points, reducing range anxiety even in rural areas.
- Environmental awareness: The population is highly conscious of climate change, viewing EVs as a responsible and practical choice.
Government targets: Policies aim for near-complete EV adoption by 2025, creating societal momentum. (World Auto Forum)
2. Which EV brand sold the most in Norway in 2025?
Tesla led Norway’s 2025 EV market with ~19.1% of new car registrations, driven primarily by the Model Y, which combines range, technology, and brand prestige. Volkswagen (~13.3%) and Volvo (~7.8%) followed closely, while Chinese brands like BYD began gaining traction. Tesla’s dominance reflects both consumer preference for range and performance and the strong charging network compatibility across Norway. (ETBrandEquity)
3. What percentage of cars in Norway are electric now?
In 2025, 95.9% of all new car registrations were electric, and in December 2025, nearly 98% of new vehicles were EVs. This makes Norway the first country in the world to almost fully electrify new car sales, surpassing even the EU average (~10–15%) and China’s EV share (~30–35%). (World Auto Forum)
4. How has Norway’s EV market evolved over the last decade?
Norway’s EV share grew from ~2.8% in 2012 to nearly 96% in 2025. Milestones include:
- 2013: EVs reach ~5% market share due to early incentives.
- 2016: EVs surpass 20% of new registrations.
- 2020: EVs account for ~54%, overtaking petrol cars.
2025: EVs hit 96%, driven by refined incentives, infrastructure, and consumer confidence. This rapid growth is unprecedented globally and serves as a model for high-income nations. (Wikipedia)
5. What policies drove Norway’s EV adoption?
Norway’s policies include:
- Zero VAT and import tax for EVs
- Reduced tolls, free parking, and access to bus lanes
- High taxes on petrol/diesel vehicles
- Government-backed investment in charging infrastructure
- Gradual phasing out of subsidies to ensure long-term market sustainability Combined, these incentives altered the cost-benefit analysis in favor of EVs, encouraging rapid adoption.
6. How does Norway’s EV adoption compare globally?
Norway’s 96% EV adoption is unmatched worldwide:
- EU average: ~15–25% of new cars electric (2025)
- China: ~35% of new car sales EV (2025)
- USA: ~7–10% of new car sales EV (2025)
- Norway demonstrates that strong policy support and infrastructure can accelerate EV adoption faster than even large, populous nations with emerging EV markets. (Reuters)
7. What challenges does Norway face with high EV adoption?
Despite success, Norway faces:
- Grid load management: Increased charging demand can strain local electricity grids.
- Second-hand EV market growth: Could affect new car sales and incentives.
- Incentive adjustments: As tax exemptions decrease, some consumers may delay purchases.
- Battery recycling and sustainability: With millions of EVs on the road, battery disposal and second-life use are critical.
8. How affordable are EVs in Norway compared to petrol cars?
Incentives and subsidies often make EVs cheaper upfront than petrol cars, despite higher battery costs. For example:
- Average Tesla Model Y price after exemptions: ~$50,000
- Comparable petrol SUV: ~$60,000 after VAT and import taxes
- Over time, lower running costs, free tolls, and maintenance savings make EVs more cost-effective.
9. Which types of EVs are most popular in Norway?
- SUVs and mid-sized EVs dominate, with Tesla Model Y, Volkswagen ID.4, and Volvo XC40 Recharge leading.
- Smaller urban EVs like Nissan Leaf are popular in cities.
- Luxury EVs are increasingly adopted as high-income households replace ICE vehicles.
10. Can Norway’s EV adoption model work in India?
Partially, yes. Lessons for India include:
- Targeted subsidies and incentives for both buyers and manufacturers.
- Investment in charging infrastructure in cities, highways, and rural areas.
- Public awareness campaigns to encourage environmentally responsible choices.
- However, India faces income diversity, grid limitations, and slower urban EV adoption, so policies need to be adapted to local contexts. (EVwire)
11. How did Tesla maintain its lead in Norway?
Tesla’s success is due to:
- Long-range EVs ideal for Norway’s rural and urban mix
- Proprietary Supercharger network for fast charging
- Advanced autopilot features and brand appeal
Early entry into Norway allowed Tesla to build brand loyalty, even as local competitors expanded
12. What is the future outlook for EV adoption in Norway?
Norway aims to fully electrify new passenger car sales by 2025–2026. Future trends include:
- Growth of second-hand EV market
- Integration of battery recycling programs
- Expansion of electric commercial vehicles and public transport
Continued leadership in green mobility policy, potentially serving as a blueprint for other nations, including India and EU countries
Summery
Norway just flipped the EV switch in 2025, with a jaw-dropping 96% of new cars sold being fully electric—basically, if you bought a new car there, it was almost certainly battery-powered. How did they do it? A clever mix of sweet incentives for EV buyers, hefty taxes on gas guzzlers, an ultra-reliable charging network, and a population that actually cares about the planet. Tesla, Volkswagen, and Volvo led the charge, while Chinese brands like BYD started making waves internationally.
Norway’s EV success isn’t just a bragging right—it’s a masterclass for the rest of the world, including India, where EV adoption is still warming up. The lesson? Combine smart policies, easy charging access, and a pinch of green culture, and you can electrify an entire nation in under a decade. Sure, there are challenges—grids need upgrading, second-hand EV markets are growing, and incentives will evolve—but Norway shows that with the right recipe, a low-emission, electric future isn’t just possible—it’s happening.

Conclusion
Norway’s extraordinary achievement—where 96% of all new car sales in 2025 were fully electric—has firmly established it as a global benchmark for EV adoption. This milestone demonstrates that with the right mix of government incentives, effective taxation on fossil-fuel vehicles, widespread charging infrastructure, and strong consumer awareness, a country can transition from traditional combustion engines to electric mobility in less than a decade.
While every market has unique challenges—such as differing income levels, urban-rural infrastructure gaps, and policy environments—Norway’s model provides a clear roadmap for countries aiming to accelerate EV adoption. For India and other emerging economies, this means:
- Implementing targeted subsidies and tax benefits to make EVs financially attractive.
- Expanding charging networks in cities and highways to reduce range anxiety.
- Encouraging public awareness campaigns that highlight environmental benefits and long-term cost savings.
- Supporting local manufacturing and supply chains to reduce costs and dependence on imports.
By tailoring these lessons to local conditions, countries can speed up their EV transitions, reduce carbon emissions, and tap into the growing global market for electric vehicles. Norway’s success shows that with policy, infrastructure, and consumer mindset working together, a fully electrified future isn’t just a vision—it’s achievable.
References & Further Reading
Here are reliable sources and links you can include in your blog post to support the data and insights on Norway’s EV milestone — all under one heading for clean SEO formatting:
• Norway’s EV Milestone & Market Data
- Norway zips ahead in EV race as car sales hit 96% electric — Reuters report detailing 95.9% EV share of new car sales in 2025, Tesla’s market role, and tax incentive impacts. Norway zips ahead in EV race as car sales hit 96% electric (Reuters)
• EV Sales & Brand Shares in Norway
- Norway’s new car sales were 96% electric in 2025 — ETBrandEquity covers Norway’s record EV sales, top brands like Tesla, and year‑over‑year figures. Norway’s new car sales were 96% electric in 2025 (ETBrandEquity)
• Networking Historical EV Transition in Norway
- EV adoption trend and historical context — Electrive article on Norway’s EV share milestones in previous years, showing growth toward dominantly electric sales. Norway Leads The Charge With 89% EV Sales in 2024 (Electrive)
• India EV Sales Growth & Stats
- India EV adoption data — EVwire tracks EV sales growth and share in India (use this to compare India’s EARLY stage with Norway’s mature market). India EV sales growth & stats (EVwire)
• Additional Supporting Insights
- Tesla’s performance and competitive EV landscape — Details on global EV market shifts and competitive dynamics (optional but useful for broader context). Tesla loses EV crown to China’s BYD (Financial Times)







